Other Question :- Troubleshooting WordPress Websites: A Guide to Identifying Problems
WordPress Page not Opening.
WordPress is a popular content management system (CMS) that powers millions of websites worldwide. While it provides a user-friendly interface and a plethora of themes and plugins, issues can occasionally arise that affect the website’s performance and functionality. In this article, we will explore how to identify problems in a WordPress website and understand the importance of the wp-config.php file in troubleshooting. By toggling the WP_DEBUG constant, we can gain valuable insights into potential issues and errors.
Understanding the wp-config.php file:
The wp-config.php file is a vital component of a WordPress installation. It contains various settings and configuration options that define how the website functions. To locate the wp-config.php file, navigate to the root directory of your WordPress installation. This file plays a crucial role in enabling debugging and identifying problems within your website.
Enabling debug mode in WordPress:
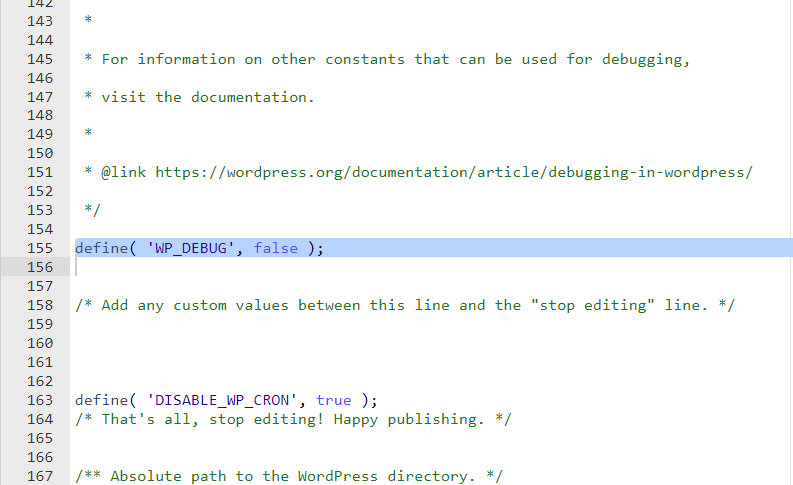
To begin troubleshooting, we can enable the debug mode in WordPress by modifying the wp-config.php file. By default, the WP_DEBUG constant is set to false, which means that error reporting is disabled. To enable debug mode, follow these steps:
- Access the
wp-config.phpfile via FTP or through the file manager provided by your hosting provider. - Open the
wp-config.phpfile using a text editor. - Search for the line that says
define( 'WP_DEBUG', false );. - Replace
falsewithtrue, so it readsdefine( 'WP_DEBUG', true );. - Save the changes and upload the modified file back to the server.
Identifying problems using debug mode:
Enabling debug mode in WordPress allows the system to display error messages, warnings, and notices, which are otherwise hidden. These messages provide valuable insights into potential issues within your website. Here are a few common scenarios where the debug mode can prove useful:
- PHP errors: Debug mode will display any PHP errors occurring on your website. These errors might include syntax errors, undefined functions, or compatibility issues between plugins or themes.
- Deprecated functions: WordPress frequently updates its codebase, deprecating certain functions in favor of newer alternatives. Debug mode can help identify deprecated functions within your website, enabling you to replace them with the recommended alternatives.
- Plugin and theme conflicts: Incompatibilities between plugins or themes can lead to unexpected behavior or website crashes. Debug mode helps pinpoint the source of conflicts by displaying error messages related to specific plugins or themes.
- Database errors: WordPress relies on a database to store and retrieve content. Debug mode can reveal database-related errors, such as connection issues, query problems, or incorrect table structures.
- Security vulnerabilities: Enabling debug mode can uncover potential security vulnerabilities by highlighting error messages related to access control, file permissions, or suspicious activity.
Troubleshooting a WordPress website can be a daunting task, but enabling debug mode using the WP_DEBUG constant in the wp-config.php file can significantly simplify the process. By setting define( 'WP_DEBUG', true );, you gain access to detailed error messages, warnings, and notices that can help identify problems within your website. Remember to disable debug mode (define( 'WP_DEBUG', false );) once you have resolved the issues to ensure a secure and optimized WordPress website. Happy troubleshooting!
(Note: While the WP_DEBUG constant is a powerful debugging tool, it is recommended to use it on a development or staging site rather than a live production site to prevent sensitive information from being exposed.)
